types of hacker
White Hat Hacker - An Overview
A white hat hacker, also known as an ethical hacker, is trained through an Ethical Hacking Certification course and utilizes hacking skills to find security flaws in devices, programs, or networks. White hat hackers follow the rule of law regarding hacking, unlike black hat hackers (or hostile hackers). Numerous white hat hackers started as black hats. The 'hats' terms are derived from classic Western films, in which heroes wore white hats and villains wore black hats. Only when it is legally permissible do white hat hackers look for flaws or exploit a system or a network.
What Do White Hat Hackers Do?
White hat hackers, sometimes known as "ethical hackers,” are cybersecurity experts who test the security of systems.
A white hat hacker (anti-cybercriminal) uses identical methods as a black hat hacker (cybercriminals) to access a system, but there is one key difference. The white hat hacker is 'allowed' to break into a system and reveal its flaws. A black hat, on the other hand, does not. Furthermore, black hats do so with nefarious motives, which are frequently motivated by avarice. As a result, their actions are illegal and subject to legal consequences.
White and black hats, in general, do the same thing: they look for weaknesses in a system. While the latter takes advantage of the loopholes for monetary or other illegal advantages, the ethical hacker alerts the system's owner to the problem. Corporations frequently engage white hat hackers to examine their systems and identify security flaws before a black hat hacker can exploit them.
Because a hack is defined as gaining access to data in a system, both cybercriminals and cyber defenders are hackers.
Many computer firms have bug-bounty programs to uncover holes in their systems, and white hats hack the system in question to uncover security flaws and earn rewards if they succeed. When you consider it, white hat hackers help businesses improve their defense and assist consumers by ensuring that their services are safe and protected.
We can all accept that a safer service would be preferable. This is why white hats are so crucial in today's digital age.
What Techniques and Strategy Do White Hat Hackers Use?
Social Engineering
Since the dawn of time, social engineering and confidence tactics have been a human culture component. Although the scheme has been modified to include technology, the principle remains the same: exploiting natural human behavior is simpler than pushing your way in. Social engineering, in ethical hacking, has become a common (and extremely effective) method of determining how accessible an organization's employees are. Cybersecurity certificate programs cover this technique and related strategies in detail.
Social engineering can help you uncover gaps and effectively handle employee security concerns when applied ethically. A social engineering mandate also aims to establish methods to enhance the international degree of confidentiality, integrity, and accessibility of your company's data.
Penetration Testing
A penetration test (pen test) simulates a cyber assault on your computing device to find vulnerable flaws. Penetration testing is frequently used to supplement a web application firewall in the area of web application security (WAF). Pen testing includes attempting to break into various application systems (e.g., APIs, frontend/backend servers) to find holes, such as unsanitized inputs that are vulnerable to code injection attacks. You can utilize the penetration tester's findings to perfect your WAF security measures, and address discovered vulnerabilities.
Reconnaissance and Research
An important step in ethical hackinCollect preliminary data.
Assess the network's coverage area.
Determine which machines are in use.
Identify open ports and access points.
Operating system fingerprinting.
Find services on ports.
Create a network map.
Programming
A programming language is a set of instructions for creating computer programs. Operating systems, data-based applications, and networking solutions are all examples of programs. To be an ethical hacker, you must have programming skills. Let's pretend you've been recruited by a corporation and given the task of penetrating their database/website (or whatever) and identifying holes in the security system. You must first know how they work, what code they utilize, and how you may change the code to perform your task.
An ethical hacker must be able to program in languages such as C, C++, Java, Python, and Perl. They can later expand their linguistic skills by learning new languages is collecting intelligence and knowing the target machine. Reconnaissance is a collection of processes and methods (such as footprinting, scanning, and enumeration) used to uncover and gather knowledge of the target device secretly.
An ethical hacker uses reconnaissance to obtain as much information as available about a target computer by following the seven procedures outlined below:
Using a Variety of Digital and Physical Tools
During security assessments, ethical hackers may encounter situations where everything appears to be in order. To put it another way, security patches, rules, network segmentation, virus protection softwares, and user awareness, to name a few, are all appropriately implemented. That's when social engineering and various other techniques become increasingly important to continue the investigation from the viewpoint of a security expert or a white hat hacker. These technologies aid white hat hackers in picking or bypassing physical locks, cloning ID access cards, installing bots and other malware, and gaining access to networks and servers, among other things.
Penetration Testers (Pentester)
Pen testers, also known as penetration testers, replicate cyberattacks on a company's network infrastructure. These authorized tests aid in detecting security flaws and vulnerabilities before criminal hackers exploit them. As a penetration tester, you'll undertake assaults on a company's current digital systems to play a strategic, offensive role in cybersecurity. These tests may employ a range of hacking skills and equipment to identify potential security flaws. You'll keep detailed records of your actions and compile a summary of what you performed and how effective you were at breaking security standards. As a penetration tester, you'll need to conduct testing on apps, network devices, and cloud services and create and execute mock social engineering attacks. You'll also investigate and test different forms of attacks, develop penetration testing methodologies, examine the code for security flaws and reverse engineer malware or spam.
Information Security Analysts
Information security analysts protect computer networks used by private companies, government agencies, and nonprofit organizations. Banking, marketing, insurance, commerce, computer systems, and many other businesses rely on data security, so there are barely any sectors where a Data Security Analyst is not required. More businesses demand the skills of a skilled Information Security Analyst as Machine Learning and predictive modeling techniques require such skills. The major role of the analyst is to develop scalable security systems to handle and prevent risks. The ethical hacking job description varies by business; however, an Information Protection Analyst is frequently on call in the event of data thefts, hacking, or other crises involving the security of digital assets. An analyst creates reports that IT administrators and company leaders use to evaluate the usefulness of their security systems. Companies will adjust security networks in response to the analyst's suggestions to ensure that the information is unavailable to unauthorized individuals. Developing and delivering instructional programs is also a part of the work, as it is frequently required to assist staff, end-users, and managers in maintaining secure security procedures.
Looking to boost your career? Discover the affordable ITIL certification price. Gain valuable skills and stand out in the competitive IT industry. Don't miss this opportunity!
Conclusion
Candidates interested in information security and with the necessary background could have little or no trouble learning ethical hacking, and you might find the right job role immediately. You can enroll today in a KnowledgeHut Ethical Hacking Certification course to stay up to date on critical cybersecurity issues and land you your dream job.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a white hat hacker called?
In cyber security, a white hat hacker is also referred to as an Ethical Hacker.
2. What is a white hat in cyber security?
A white hat hacker, also known as an ethical hacker, employs hacking skills to find security flaws in devices, programs, or networks.
3. Are white hat hackers good?
Unlike the Black hat hackers, white hat hackers try to secure the data by finding loopholes in a company’s network or devices.
4. Where does the term white hat come from?
Hackers are categorized in a 'Wild West' reference where ‘White hats’ were the good guys, and ‘Black hats’ were the bad guys.
5. Where do white hat hackers work?
White hat hackers utilize their skills to find security flaws to protect enterprises from malicious hackers. They can be paid staff or contractors who work for corporations as security professionals looking for security flaws.
Black Hat Hacker
What is a Black Hat Hacker?
Dark cap programmers frequently start as fledgling “script youngsters” utilizing bought programmer devices to misuse security slips. Some are prepared to hack by supervisors anxious to bring in cash rapidly. The prominent black caps will, in general, be gifted programmers who work for complex criminal associations, which in some cases give joint effort apparatuses to their laborers and offer assistance arrangements to clients, very much like real organizations. Dark cap malware packs sold on the dark web once in a while even incorporate guarantees and client support.
Dark cap programmers frequently foster fortes, for example, phishing or overseeing far-off access apparatuses. Many get their “positions” through gatherings and different associations on the dull web. Some create and sell vindictive programming themselves; however, others like to work through establishments or renting courses of action – once more, as the authentic business world.
Hacking has become an essential insight gathering apparatus for governments; however, it is all the more entirely expected for dark cap programmers to work alone or with coordinated wrongdoing associations for pain-free income.
White Hat vs. Black Hat: What’s the Difference?
The principle distinction between the two is inspiration. Not at all like Black hat programmers, who access frameworks wrongfully, with vindictive purpose, and regularly for individual addition, white hat programmers work with organizations to assist with recognizing shortcomings in their frameworks and make relating refreshes. They do this to guarantee that dark cap programmer can’t get to the framework’s information illicitly.

How do Black Hat Hackers break into systems?
There are various kinds of dark cap programmers, from the individuals who act alone to the individuals who work inside huge, profoundly beneficial digital wrongdoing associations. Many dark cap programmers began as alleged “script youngsters,” who set off to abuse security weaknesses then, at that point, developed their procedures to bring in fast cash.
The upper levels of the dark cap security world are talented programmers working for complex digital wrongdoing associations, which work similarly to genuine organizations. These associations have accomplices, affiliates, and merchants with whom they purchase and sell malware licenses for use by other criminal associations throughout the planet.
Dark cap programmers convey a broad scope of methods to target and assault casualties. A few hacks are fast and mechanized, utilizing bots that wander across the web looking for unprotected gadgets and programming weaknesses. Different assaults result from social designing and profoundly complex strategies, for example, phishing assaults that spread malware and malignant connections and connections.
Laws against hacker attacks
If you think your personal information is safe, think again. Cybercrime is a growing trend that has grown over the past few years. People who are victims of cybercrime often have their identities stolen, private photos shared without their permission, and accounts hacked.
But what can be done about these crimes? You can report them to the police, but if they don't act fast enough or if you're too afraid to press charges, you might want to try hiring a professional hacker. These hackers are skilled at finding ways around various security measures in order to infiltrate computer networks and steal private data. If they find any weaknesses in the security system, they will patch them up before moving on to their next target which is usually a competitor's network.
Hacking falls under the category of computer crimes, which is why jail sentences can be imposed if convicted. This type of activity is illegal in most countries, so it’s important to know your rights and also the laws surrounding hacking.
The Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) is a joint venture between the FBI and the National White Collar Crime Center. This organization was created to help law enforcement agencies deal with cybercrimes that involve hackers. According to the IC3 website, there are 10 things you probably didn’t know an average black hat hacker could do:
Hack into a company’s network with ease. They often have physical access or remote access to networks without being detected or traced.
Steal credentials from your system. They may use stolen passwords or log in credentials in order to access accounts on other systems.
Steal information from your smartphones. Whether it be text messages, calls, or even GPS locations.
Use spyware applications to monitor employees. They can view everything your employees do on their computers when they're not looking.
Copy data from one computer onto another. This includes breaking into the system remotely and then transferring all of its files onto another device.
Access your personal information. Such as phone numbers, addresses, and bank account numbers.
Hijack search engine results. The best way to mess with someone else's life is through their online searches.
How to protect yourself from Black hackers
Black hat programmers represent a significant danger to associations’ information, frameworks, organizations, and clients. In any case, there are safety efforts that organizations can execute to endure dark cap programmers’ evil activities. These actions are routinely examined by moral hacking specialists at Black Hat gatherings.
- Firewalls
Firewalls are principally pivotal to ensuring the border of associations’ organizations. Firewalls shield associations from both inside and outer digital dangers. The channel network traffic gives further substance review, which distinguishes and impedes malware and progressed security hazards.
- Content Filters
Content channels go about as guards for business clients and can be designed to permit or forestall admittance to explicit sites. This is essential to forestalling dark cap programmers from driving casualties to vindictive sites or acquiring a passage point into corporate organizations.
Interruption Prevention System (IPS) identify likely interruptions to organizations or workers and make a move to forestall them.
- Worker Hardening
Worker machines can run excessive benefits for them to capacity and present a weakness that dark cap programmers could abuse. For instance, a mail worker could run File Transfer Protocol (FTP), and a web worker may run a Telnet administration, which is both intrinsically secure. It would be best if you took out these pointless administrations to limit the chances for programmers to misuse corporate frameworks.
- PC Use Policy
Associations can fortify their frameworks by forcing PC strategies for their representatives to follow. The security innovation illustrated above, like substance channels, IPS, and firewalls, execute decisions that characterize PC utilization arrangements. In any case, an arrangement likewise needs to cover how representatives are required to utilize PCs, email, and the web, just as the results of abusing the strategy.
- Security Testing
Progressively refined dark cap programmers continually look for weaknesses that empower them to abuse corporate frameworks and take touchy information. Associations should keep pace through moral hacking, constantly observing their organizations, and testing their frameworks for new weaknesses. This incorporates running regular entrance tests and weakness filters that recognize and relieve likely dangers.
- Representative Training
An association is regularly just as secure as its representatives permit it to be. Workers need to follow security best practices, like the protected utilization of email and other online administrations. Likewise, they ought to get ordinary network protection preparation that educates on the signs regarding cyberattacks, data about the most recent digital dangers, and reminds them about the association’s PC use strategy and the outcomes of a penetrate.
The most famous black hat hackers
Quite possibly, the most well-known dark cap programmer is Kevin Mitnick, who, at a certain point, was the most needed cybercriminal on the planet. As a dark cap programmer, he hacked into more than 40 large companies, including IBM and Motorola, and surprisingly the US National Defense cautioning framework. He was consequently captured and spent time in jail in prison. However, he turned into a network safety specialist who utilizes his hacking information for white cap hacking purposes following his delivery.
Another notable model is Tsutomu Shimomura, who is a network safety master credited with finding Kevin Mitnick. A computational physical science research researcher, Shimomura likewise worked for the US National Security Agency. He was one of the primary analysts who previously brought issues to light of mobile phones’ absence of safetry and protection. The originator of Neofocal Systems utilized his security abilities for moral purposes and assumed a vital part in dealing with Kevin Mitnick. His book Takedown was subsequently adjusted to a film called Track Down.
Conclusion
Most digital lawbreakers have any desires for monetary benefit by holding another person’s information “prisoner” and requiring pay as a payoff or utilizing accreditations to access a ledger that isn’t theirs. Another explanation may be for the unadulterated rush of practicing their abilities and information in the presentation of illicit demonstrations.
Grey Hat Hackers
What is Gray Hat Hacker?
Today, the legal system and information security stay in a bind, and the gray hat hackers remain in between. Being one of three primary hacker types, the individual or team of hackers penetrates a website or services without the motive to leverage benefits.

The Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) points out federal laws compromise computer network security. The gray hat hackers follow the line of ethics and law in preserving a secured environment without constant payroll.
Exposing security risks and challenges is crucial for companies to get the ‘ground truth.’ Organizations help ethical hackers or penetration testers perform these attacks in simulations. Though these are done in a controlled way, it’s good enough for the real world. But everyone has their limitations. Even if you’ve fixed every nook and corner, chances are there is a loophole. It’s just a matter of time till someone finds it.
The job of a gray hat hacker is to find these weak points and attack. Though they don’t attack to compromise, it’s not just for the chills and shivers.
Though a typical hacker may try to penetrate and gain enough leverage on the system, a gray hat hacker does things professionally and ethically. It takes time to plan out an attack, form a team if needed, target the subject and execute the attack. And it’s not done yet. Later, this information is sent to authorities to fix the issues without causing damage to customers.
Unethical Hacker Vs. Gray Hat Hacker
Many imagine hackers are famous for bad stuff related to computers. But as you’re here, we believe and know that’s not the case for you. But the characteristic of an unethical hacker remains present in the hacking environment. Here are some of the ways we may define unscrupulous hackers:
An unethical hacker selects a target and does damage for fun or profit. Without care for rules and the bound of targets, the unethical hacker has multiple simulations of attacks. It is hard to trace back to the attacker as many systems are at their disposal. Open-source intelligence gathering, fingerprinting, active scanning, escalating privileges can be seen as parks of being an unethical hacker.

Anyway, a gray hat hacker will not hold exploits to gain leverage later. So, privilege escalating is only handled by unethical hackers. On the other hand, gray hat hackers may nominate themselves or take the claim on vulnerability exposure and take the fame.
Why are Gray Hat Hackers important?
Though we did not go through all types of hacker variants in this article, it is still important to realize there are a lot of personalities fueling the passion of hacker types. We have white hat hackers trying to protect organizations or services from malicious intent. Black hat hackers will go the extra mile to conquer and make organizations, individuals’ victims. The fight is always on the run beyond the cover of the internet’s barrier.

Then we have gray hat hackers, a variant in between, hacking to find vulnerabilities without taking advantage. If we look for an example, a specific product-market can be justified. There are great products, and there are okay products. Customers try to get the best ones but can sometimes afford only the good ones. And there is another type, trying to compete with them, keeping the price tag competitive, and finding new ways to improve.
Gray hat hackers are pretty similar. Safely accessing banking systems, mobile apps, secure transactions may have flaws that organizational pen-testing employees do not detect. Those would cause a significant threat if gone to an extent without the glimpse of gray hat hackers.
Do we reward or punish Gray Hat Hackers?
What would you do if someone broke into your home to tell you the system is weak? Of Couse, you’d be mad just like the next guy. In that sense, gray hat hackers can be hard to tolerate.

But if we take it to an advanced level, where companies could suffer losses in millions of dollars and lose sensitive information about customers, we can lessen up a little bit. Organizations offer bug bounty programs targeted at gray hat hackers, where they can show off their skills and get rewarded at the same time. What’s the best benefit to gain here? You’re not breaking any law as a gray hat hacker by participating in bug bounty programs or taking permission beforehand.
Nowadays, bug bounty programs have become much popular. You can find more information about bug bounty programs on Hackerone, Bugcrowd, Microsoft’s bug bounty program, Google’s bug bounty, and many more.
Script Kiddies
Script kiddie definition
"Script kiddie" is a demeaning term used to describe novice hackers who use existing scripts and software to carry out cyberattacks.
Cybersecurity statisticsshow that there are around 2,200 cyberattacks per day.
But who's actually behind them? Turns out, hackers fall on a spectrum of experience levels from advanced to novice — script kiddies are on that novice end, but are no less dangerous.
You can think of a script kiddie as someone who has stumbled across a superhero suit. While they may not be able to do as much as the superhero themselves, they suddenly have access to more power than they know what to do with.
This can be dangerous, as their reckless attacks and lack of experience can cause real damage and may even get them into trouble.
Continue reading to learn more about script kiddies, how they work, and how you can help protect yourself.
How script kiddies work

As the term suggests, script kiddies, also known as skiddies, utilize prewritten scripts and software to carry out their hacking endeavors. Experienced hackers, on the other hand, may write their hacking scripts from scratch, custom-built for their intended target.
Believe it or not, the internet is flooded with prewritten hacking scripts and hacking tools available for use or purchase, making it easy for amateur hackers to find the specific hacking script they’re looking for. These include password attack tools and denial of service (DoS) tools.
With that being said, there is no guarantee that a prewritten script will work how the script kiddie hopes. This can cause them to fail at achieving their hacking goal or may lead them to do more damage than they ever intended.
It's important to remember that not all low-level hackers are script kiddies. Other types of hackers may try to learn the basics of hacking rather than relying on premade scripts.
Characteristics of a script kiddie
Now that you’ve answered the question “What are script kiddies?” and have learned how they work, let’s take a look at some of the common characteristics of a script kiddie hacker and their attacks:
Inexperienced: In many cases, skiddies will have little to no technical computer skills.
Indiscreet: Because most script kiddies do not know how to mask an attack, their attacks will likely be detected much faster than one carried out by an experienced hacker. This may lead cybersecurity experts or law enforcement to easily discover their identity.
Reckless: Due to their lack of technical knowledge, script kiddies may run a prewritten script that could end up causing more problems than they expected.
Impulsive: Script kiddies often act impulsively, using whatever prewritten script they can find for fun rather than having a specific motive.
Attention-seeking: In some instances, skiddies may look toward hacking as a way to gain notoriety, hoping that carrying out a cyberattack can help them capture attention from their peers or the news.
Of course, not all script kiddie hackers are alike, and their intentions may vary. After all, the impact of a script kiddie attack depends entirely on the quality of the hacker’s script they use.
Script kiddies vs. elite hackers: What’s the difference?
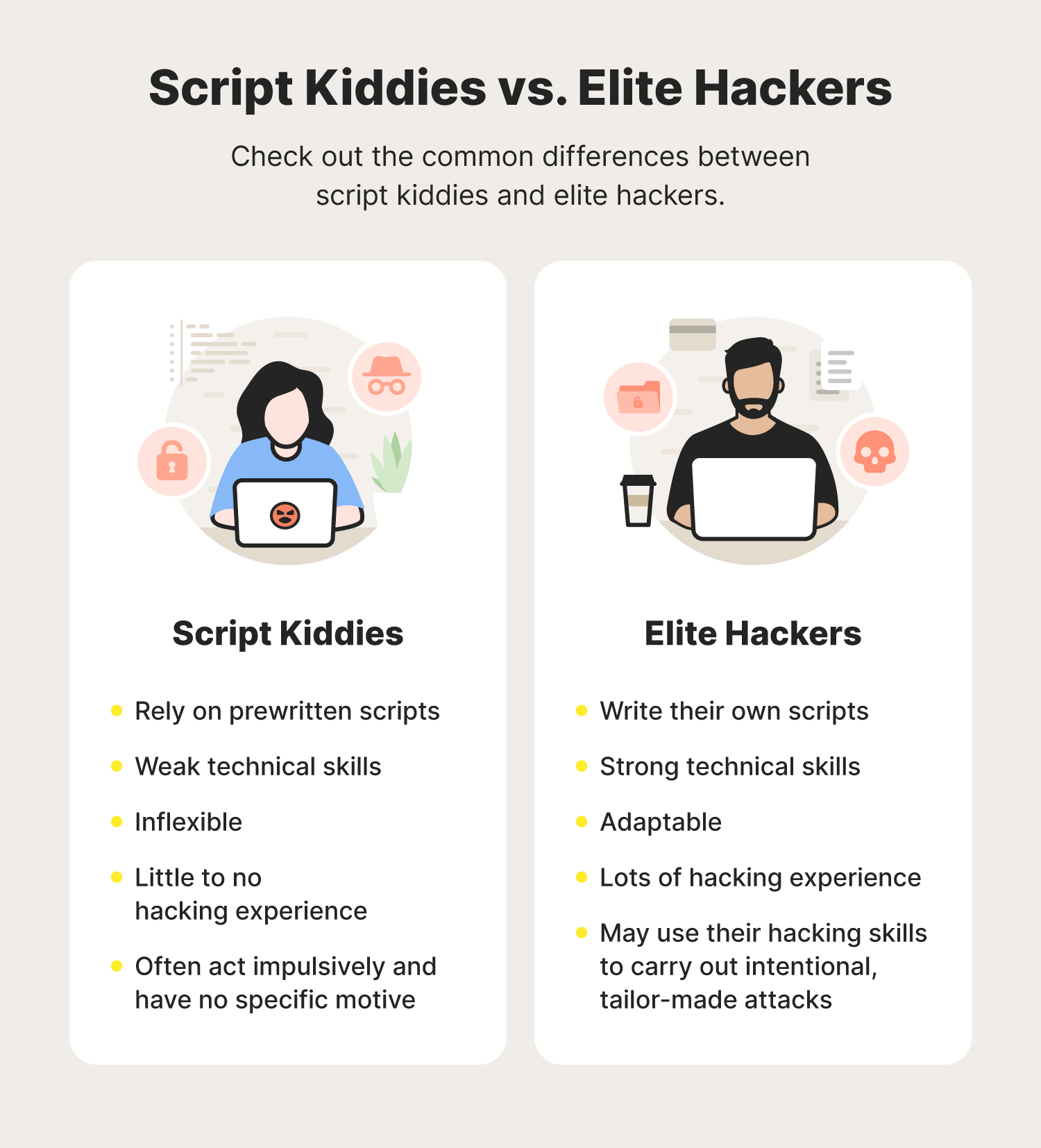
With the traits of a script kiddie in mind, you may wonder how they differ from elite hackers. Script kiddies and elite hackers differ in three main ways:
Skill level: Unlike script kiddies, real hackers are much more skilled. These experienced hackers write their own customized scripts based on the type of hacking they wish to partake in. On the other hand, script kiddies are limited to whatever they can find online.
Intention: Script kiddies often carry out attacks for notoriety or simply the thrill of it. Alternatively, elite hackers often have much more meaning behind their attacks, spending large amounts of time formulating their scripts. Depending on the type of hacker, these experienced individuals may use their skills for different reasons, from working as a cybersecurity professional to carrying out ransomware attacks for monetary gain.
Experience: Lastly, elite hackers have hacking experience that skiddies likely do not. This additional experience helps elite hackers cover their tracks and protect themselves during hacking exploits. Additionally, experienced hackers can use their technical knowledge to adapt on the fly and respond to obstacles that may get in their way.
To sum up these differences, elite hackers are highly skilled and write hacking scripts from scratch, whereas script kiddies are inexperienced and exploit scripts written by elite hackers.
Script kiddie attack examples
Although script kiddies are known for their lack of skills, they may still be able to do some serious damage if using a high-quality hacking script. Here are some examples of common attacks that can be carried out by script kiddies:
Website defacement: Often for trolling purposes, a script kiddie may use a hacking script to penetrate a website and alter or delete its existing content. This is an easy way for a script kiddie to do something that people will quickly notice.
DoS attack: A DoS attack is an attack that floods a website, device, or network with traffic, either causing it to malfunction or crash. Script kiddies can find premade hacking software that allows them to easily perform these attacks.
Social engineering attacks: Social engineering is the act of manipulating individuals to give up sensitive information for malicious purposes. Script kiddies may use social engineering tactics in tandem with a kiddie script to complete different types of phishing attacks or distribute malware.
In some cases, script kiddie attacks can have devastating real-life consequences and could even lead to jail time. For example, a 15-year-old script kiddie used a DoS attack to hack the telephone company TalkTalk in 2015. This attack led to a data breach, and eventually the arrest of the 15-year-old boy.
How to avoid script kiddies: 9 cybersecurity tips
Even though script kiddies may not be the most dangerous hackers, it’s still important to stay cautious and keep your Cyber Safety in mind. To help protect yourself from script kiddies and other types of hackers, follow these tips:
Safeguard your personal information: No matter where you are online, always think twice before sharing any personal information. Be it your phone number, birthday, or address, a script kiddie and other hackers could use phishing emails to trick you into giving up this information so they can use it for malicious purposes such as identity theft.
Enable two-factor authentication (2FA): Using 2FA can help minimize the risk of a script kiddie or other hackers gaining access to your accounts. That way, even if a hacker finds your password, they will run into another obstacle before accessing your accounts.
Use strong passwords: In some cases, script kiddies may be able to purchase files containing user credentials on the dark web. Once the hacker receives these credentials, they may use them to carry out password spraying or credential stuffing attacks. To avoid this, always use strong passwords and regularly change them to help stay secure.
Back up your data: As a protective measure, it's beneficial to regularly back up your data. That way, if you’re affected by a script kiddie or any other type of cyberattack, you’ll know your data is safe in a second location. Not only that, but having a data backup can help you if your device is lost, stolen, or broken.
Secure your mobile devices: It’s important to remember that your mobile devices may also be at risk of hacking. To help minimize your risk, always set a security PIN on your device, keep your operating system up to date, and avoid third-party app stores.
Avoid suspicious links and attachments: A script kiddie may disguise their malicious files behind a link or in an attachment, usually in a phishing email or smishing text. Avoid clicking these at all costs, as you may accidentally infect your device or visit a malicious website.
Keep your operating system up to date: Software updates commonly contain security patches and bug fixes that may help stop a script kiddie or other hackers in their tracks. To ensure your device is always protected, update your operating system regularly.
Consider using a VPN: Using a VPN can help enhance your privacy by encrypting your online traffic. In addition, the use of a VPN can help disguise your IP address and may make it more difficult for script kiddies to use malicious software such as spyware against you.
Use antivirus software: When it comes to hacking, you can think of antivirus software as an extra line of defense that can help minimize the risk of script kiddies and their associated attacks. From removing malware to flagging suspicious behavior, installing antivirus software is a great way to boost your Cyber Safety.
By prioritizing good cyber hygiene, you can reduce the risk of being affected by a script kiddie or other types of hackers. To better protect yourself, take the time to learn how hackers access your computer to ensure you have all your cybersecurity bases covered.
FAQs about script kiddies
Still wondering about script kiddies? Read through the answers to these common script kiddie questions.
What is the origin of script kiddie?
The exact origin of the term “script kiddie” is unknown. Early uses of the term started appearing in hacker message boards and blogs in the mid-1990s. Since then, it has become much more popular and was even used several times in the popular hacker show “Mr. Robot.”
Are script kiddies dangerous?
In short, yes. While they may not have the skills to carry out advanced attacks like experienced hackers, script kiddies can cause serious damage when armed with the proper hacking scripts, from distributing different types of malware to DoS attacks.
Are script kiddies common in gaming?
In some instances, script kiddies may infiltrate the gaming community. Examples include stealing hacker scripts to help them cheat or carrying out a DoS attack to shut down a gaming server.
What is the goal of a script kiddie?
While the goal of a script kiddie can vary from case to case, many script kiddies take up hacking to gain notoriety or impress their peers. In other cases, the script kiddie may be carrying out their attacks just for the thrill of it.
What tools do script kiddies use?
Script kiddies rely on prewritten hacking scripts and script kiddie programs developed by experienced hackers. Some examples of script kiddie tools include malware, DoS tools, and password-cracking tools. In addition, script kiddies may rely on these tools paired with social engineering tactics to help manipulate their targets into giving them the information they’re looking for.
State Sponsored Hackers

Every day, thousands of cyber-attacks are launched against Internet users all over the world. Researchers have developed a variety of defense mechanisms in response to these attacks. Currently, the techniques used among cyber-attackers to carry out attacks become affected by the human exploit. Such attacks are more common than in the past, and they are more difficult to manage.
Traditional security countermeasures are incapable of preventing breaches that target people. This paper examines the history, current state of cyber security threats, countermeasures, and defense tools that are relevant to daily online activities. It provides a useful cyber-attack definition and classification that helps in the recognition of cyber-attacks and cyber-security measures. Existing cyber-threat and risk management schemes are assessed against three of our criteria for effectiveness: responsiveness to countermeasures against cyber-attacks, real-time assistance, and needs-based intervention, and training and educational materials to raise user knowledge.
Introduction
Our digital culture can be used and abused in ways that are antithetical to our ideals, as more people realize. There is also a clear recognition that we are dealing with highly sophisticated state-sponsored attacks aimed primarily at financial gain. The attackers’ abilities, size, and determination are all increasing. That is the exact reason why “state-sponsored cyber-attacks and attackers” is an emerging topic in 2021.
Aside from hackers seeking to make money by using stealing private and company information, entire realms at the moment are the usage of their hacking abilities to penetrate different governments and launch attacks on critical infrastructure. Cybercrime is the main subject nowadays, now not only to the personal sector and people but also to the government and the entire USA.
Many of those assaults target government's very own applications and infrastructure, but private agencies are also prone. nation-subsidized cyberattacks are a growing and serious threat to the personal corporations, in step with a take a look at from Thomson Reuters Labs. nation-sponsored cyberattacks will increasingly threaten the one's sectors of the business world that provide handy targets for settling geopolitical grievances.
Evolution of the topic
What is a cyber-attack?
A secret mission to damage computers, steal data or use a database server to perform attacks is referred to as a cyber attack. Malware, phishing, ransomware, and man-in-the-middle attacks are just some of the ways cybercriminals will mount a cyber assault. Organizations remain vulnerable to cyberattacks as a result of intrinsic and residual threats. Cyber threats may also be utilized in cyber warfare or cyber terrorism by nations and states.
By breaking into a vulnerable device, a cybercriminal may take, change, or kill a specific target. Cyber-attacks can range in complexity from malicious software such as malware or a ransomware attack on a small business to try to bring down-sensitive infrastructures such as a city government or government institution such as the FBI or Department of Homeland Security. A data leak, in which confidential data or other private information is leaked, is a typical byproduct of a cyber-attack.
If more businesses put their most sensitive details online, the need for information technology experts that understand how to control risk with information to mitigate cybersecurity risk. Vendor risk management and third-party risk management systems are now more relevant than ever, thanks to the growing usage and regulatory emphasis on outsourcing.
Types of cyber-attacks.
1. Un-targeted attacks
Attackers use un-targeted attacks to reach as many computers, systems, or users who are Infront of devices as possible. They use to do this by using strategies and using their practices that take advantage of the freedom in the world wide web. Such as:
· Scanning — Randomly hacking large areas of the internet.
· Phishing — Sending emails to a group of people with the purpose of gathering personal information such as bank account details by directing them to a spam website.
· Ransomware — Spreading executable files that encrypt disks.
· Water holing — Creating a fake website or compromising a real one in order to take advantage of visitors.
Targeted attacks
It could take a time to set the foundation for the attack so that they can find out the best and the fastest way to execute their exploit directly to user’s networks. The targeted attack can be more harmful than an untargeted attack. Because it has been clearly targeted and designed to attack the firewalls, programs, or databases. Examples of targeted attacks are:
· Make use of botnets — to deliver a DDOS attack (Distributed Denial of Services)
· Spear-phishing — sending emails to targeted people that can attack malicious software or a link that can download malware.
· subverting the supply chain — To attack companies’ supply of equipment or applications
2. What do cyber-attacks target?
Cyber-attacks are directed at a physical or logical resource that has one or more flaws that a cybercriminal may manipulate. The resource’s confidentiality, honesty, or availability could be jeopardized as a consequence of the assault.
Harm, data exposure, or control of resources can stretch beyond the one initially defined as vulnerable in certain cyber-attacks, such as obtaining access to an organization’s Wi-Fi network, social media, operating systems, or personal information such as credit card or bank account numbers.
The CIA triad (confidentiality, honesty, and availability) is the foundation of information security.
What are state-sponsored cyber-attacks?
States can hire hackers directly through their militaries and government agencies. They will also be able to finance them in a more indirect manner. If the attack is identified, this would be easier to ignore the county’s interest. As a result, the political fallout from these attacks could be reduced. It further blurs the distinction between criminal and government organizations. The state-sponsored units then go after their funders, enemies for various reasons.
In today’s hybrid warfare, cyberattacks have become a necessary component. It encompasses a wide range of aggressive actions used to achieve objectives. Conventional ground campaigns, cyberattacks, disinformation, and funding local separatist forces are both examples of hybrid warfare. Russia, for example, has recently used such tactics against Ukraine.
Private companies that engage in touchy sports or guide authorities’ systems are definitely as possible to come back lower back below assault as public establishments. The identical is genuine for non-earnings and regulatory our bodies.
For example, the recent cyber attacks on the US Democratic National Committee not only did the attackers stand to obtain strategically significant information, but they also displayed their potential to impact a national election. Aggravating the Clinton email issue and exposing the Democratic Party’s internal power struggles.
Because the present-day Russia-primarily based definitely hack through manner of so-known as FANCY endure at the area Anti-Doping corporation suggests, a hobby that is deemed to harm the Russian countrywide person is responsible to call down a retributive country-sponsored assault — in this case, as revenge for banning Russian athletes from the Olympic and Paralympic games for drug use.
State-sponsored attacks, on the other hand, are not limited to power centers like the Kremlin and the Pentagon.
Genuinely, being visible to aid a selected nation’s interests can put a corporation in severe hazard of assault. Organizations of a wide variety want to be aware of this powerful form of threat — the days when groups had nothing worse to worry than enterprising fraudsters are lengthy long past it’s far important that security administrators have the information and the gear to defend their organizations towards state-brought on cyber threats. To do that, they need to first recognize the important thing behaviors of nation-subsidized hackers.
Origin of state-sponsored attacks
There is no single event that has been identified as the start of cyberwarfare. However, the Morris worm, which infected the emerging cyberinfrastructure in 1988, is widely regarded as the first to cause cyberwarfare, according to the North Atlantic Treaty Organization. The worm spread by taking advantage of flaws in the way UNIX transfers mail and anticipating poor passwords.
In the history of cyber warfare, “Stuxnet” is often regarded as one of the first powerful computer bombs. The Stuxnet virus was used by Israel and the United States to destroy a nuclear enrichment plant in Tehran as part of their “Operation Olympic Games” mission.
Before Stuxnet, hackers and cybercriminals were the main concerns of cyber security. Typically, they are motivated by monetary benefits. State-sponsored cyberattacks aren’t really motivated by money. As opposed to rogue hackers, state-sponsored criminals have much greater capabilities.
In 2001, Russia conducted a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack against Estonia, disrupting connectivity and forcing major websites across the world to go offline. Similarly, several cyber warfare attacks have occurred, and the number and severity of these incidents are projected to continue to escalate in the future.
Reading about history, Stuxnet is a remarkable thing that changed the path of state cyber warfare.
What is this “Stuxnet” virus?
Stuxnet is a computer worm meant to target Iran’s nuclear plants but has since developed and spread to other manufacturing and energy-producing facilities. The first Stuxnet virus attack was aimed at programmable logic controllers, which are used to automate computer processes. It was the first identified virus that can damage the hardware. It appears to had been developed with the aid of the United States countrywide security enterprise, the CIA, and Israel intelligence after it. Becomes started in 2010.
A 500kb worm corrupted the software of at least 14 Iranians industrial sites including the uranium enrichment center. A worm spreads on its own, mostly over a computer network. Unlike a computer virus that requires a victim to install it.
Who created Stuxnet?
The intelligence services of the United States and Israel are generally believed to have developed Stuxnet. “Operation Olympic Games” was the code word for the classified initiative to produce the worm, which began under President George W. Bush and was pursued under President Barack Obama. Although no country has ever publicly admitted to creating Stuxnet, a 2011 video commemorating Israeli Defense Forces chief Gabi Ashkenazi’s retirement mentioned Stuxnet as one of his accomplishments.
What did this warm do?
Stuxnet is said to have induced numerous centrifuges at Iran’s Natanz uranium enrichment plant to flame out. Other agencies changed the virus through the years to make it attack infrastructures which include water systems, fuel lines, power plants.
This worm was an incredibly advanced and malicious piece of software that operated in three stages. It started out by copying itself on Microsoft Windows machines and networks. The company then went looking for Siemens Step7 software, which is also Windows-based and used to configure industrial control systems that run centrifuges. Finally, the programmable logic controllers were harmed. The writers of the worm could therefore monitor production processes and even trigger the fast-spinning centrifuges to break themselves apart, all without the knowledge of the plant’s human operators.
And some resources said that Stuxnet was a multi-part worm that spread through Microsoft Windows computers via USB drives. The virus looked for signs of the Siemens Step7 program, which is used by industrial computers acting as PLCs to automate and control electromechanical machinery. The malware assault upgraded its code over the internet after locating a PLC device and started transmitting damage-inducing instructions to the electro-mechanical equipment the PC operated. Continuously, the virus gave the key controller false information. There would have been no sign of a concern until the device started to self-destruct, according to someone monitoring the equipment.
What classifies as a State-sponsored hack?
When it comes to government hacking, one of the most challenges businesses face is determining if a given attack started from the government at all. It is extremely difficult to trace the source of an attack in this method which is known as “attribution”. The problem is made worse by the fact that many government hackers will try to disguise their attacks as those carried out by hackers called “freelanced hackers”, and that many countries use outside hacking firms to maintain deniability.
The “attribution problem” has been meant to describe this situation. While determining who launched an attack may appear to be a simple process, a key notation in cyber security and digital forensics is that identifying a criminal after a hack may be extremely complex. Hackers are a wealth of technical tools at their disposal to help them hide their activities. Even if analysts are able to configure which computer a hacker used, pinpointing the exploited person is hard.
Here is a real-world example that happened in 2014. When the Barak Obama administration claimed North Korea for the Sony Pictures attack many of the security industry believed, but there was also some significant doubt. Part of this was due to Obama’s failure to reveal that the US had direct access to North Korean internet traffic before and during the Sony stack. The New York Times later reported on this information. Individual and civilian security organizations may find it difficult to access government attributions due to the variations of access to comprehensive evidence.
Top exploit methods used by state-sponsored hackers
We have two challenges when It comes to discussing the exploits and strategies guided by state hackers. One is the techniques used by 66 state hackers are kept secret. The other one is, when it comes to deploying attacks, each country has various motivations for the hackers and hence employs different methods.
Leaks from the US government are another source of information related to state hacking. Wikileaks released a massive portfolio of CIA reports called Vault 7 and they give a fascinating look at the US government’s techniques. The researchers have found a stunning pattern of security errors at one of the world’s most secretive corporations, yet the fundamental flaws that led to the breach are all too common in today’s companies.
However, there are few methods to learn more about how state hackers work. Verizon company has shared information about this in a part of its annual reports. State hacking has grown dramatically in recent years. According to those reports, this is how the most typical method employed by state hackers.
We can give a bit more insight into these state-sponsored attacks assaulted by examining various sources of information on the exploit methods deployed by government hackers and by slicing the raw data that the data breach investigation report gives. The top six attack techniques deployed by the state hackers are given in the table above. These 121 breaches, according to the chart are based on well-practiced attacks in which particular activities virtually invariably appear.
This virus then communicates with the command and control(C2) server for a foreign authority. The C2 server tells the backdoor to do a few simple tasks, such as looking through a file system and then exporting data that are of interest. A foreign government looking for a collection of password hashes so that it may perform a reverse lookup and remotely hack into these accounts.
Yes. Definitely, for a more skilled form of a non-state hacker, this is not an unusual scenario. The important element to remember here is that standard preventive measures and plan B style mitigation would be still effective.
Security Risks of State-Sponsored hacking
If your profession is working in a security team for a non-state commercial business, you might think that global hacking is not a big matter. This is not the problem at all. Any type of vulnerability should not be considered as lightly. Whether for security testing, law policies, or any other reason. Hacking information, attacking resources without the user’s acknowledgment is always assault from a technical standpoint, regardless of the purpose. Inactive communication, device networks stream can be damaged or drop the security level as a result of an attack.
1. One target can turn into many.
Although state hackings are supposed to be targeted hack and surgical. Attacking methods and exploits may be used against a wide range of devices and software. Even if they were designed for a single task, exploits may be exploited by the state for a variety of objectives, including cyber-attacks by some kind of advanced persistent threat actors (APT) manage by the government.
As an example, the Stuxnet worm which I mentioned above was deploying to eliminate Iranian nuclear centrifuges. But it sprayed throughout the world damaging millions of computers.
2. Passing state rules and regulations.
With the possibility of mistakenly accessing or manipulating a foreign country’s network system, which might be considered as an attack on the country. Its interests or its residents, with all the political, economic with cyber attack probability.
3. Exploits can be copied, leaked, or stolen.
Even the most secure government state has been hacked. Some 3rd party hackers called “Shadow Brokers” hacked the US national security department and publicly released the zero-day exploit called “EtarnalBlue” in 2015, while the Italian security firm hackers were also hacked as a result of copying exploits.
4. Distrust of the hired hackers.
In last year, security researchers revealed that the NSO group’s software, which is utilized by various governments, was used to discreetly break WhatsApp user accounts of journalists and active contributors to monitor their transactions and communications.
Fine targeting of State-Sponsored hackers
Hackers who were sponsored by the government are frequently identified by their commitment to a single target. Illegal hacking is typical as possible in order to improve the possibilities of someone accidentally clicking on a phishing email link or transferring money. State hackers, on the other hand, are more likely to have a specific high-end target in mind and, as a result, will invest more time and effort to locating and exploit.
The WADA attack, for example, was accomplished through an effective spear-phishing effort in which phishing emails were carefully customized to that specific organization, providing facts and inside information that caused staff to believe the messages were authentic and trustful.
Then unfortunately they access or install harmful documents or software. Another example is the CEO scam. Which an employee receives an email pretending to be from the company’s CEO and is asked to send money to the attacker.
To overcome this, businesses must ensure that they have strong communication standards in place and instruct their staff on the sorts of email they may anticipate from management, as well as what is likely to be harmful. Any abnormality should be treated with suspicion.
Most dangerous state-sponsored hackers and their contributions
Advanced persistent threats(APTs) are the term used by security experts to describe these hackers. Some organizations give them a number to work with. Others use other naming practices, referring to organizations supported by various regimes as different animals, such as Iran’s calling card, which is a kitten.
1. Cozy Bear (APT29)
Region: Russia
Best known for Covid-19 vaccine data theft, Pentagon attack in 2015, FireEye and SolarWinds hack
Playing a crucial role when Russian hackers try to sway the 2016 US presidential election. Since its alleged beginning in 2008, the group has targeted a wide range of institutions including governments data stores, telecommunication businesses, energy corporations, and even cybersecurity businesses in the pattern that suggest it is using techniques similar to those used by state security agencies. After all, Cozy Bear is one of two state-sponsored hacking organizations affiliated to the GRU, Russia’s main military intelligence organization, according to experts.
2. Lazarus Group (APT38)
Region : North Korea
Best known for Covid-19 data theft, Operation Troy, WannaCry attack
Also known as Hidden Cobra, Zinc and North Korea’s lone commercial venture is well known hacking outfit supported by Pyongyang. North Korea has been butting a lot of money into its cyber warfare skills and it’s paying off. The Lazarus group has been tied to some of the most damaging cyberattacks in recent years, including the famous WannaCry ransomware attack in 2017. Which went through over 300,000 machines all around the world and netted the rogue state government unfathomable sums of money in ransom payments.
3. Double Dragon (APT41)
Region: China
Best known for 2020’s huge global hacking effort
Also known as Cicada, is a Chinese state-sponsored organization that also dabbles for personal gain because of a sponsor by someone with the huge amount of money. The group’s actions date back to 2012 and involve attack operations against 14 nations including the US and UK.
Unfortunately, five members of their gang were identified and arrested in September 2020 as a mission of biggest United States cyber-attack on when Chinese hackers try to phishing on US servers. But they have said that it is not the end of their attacks and more to come against the United States.
4. Helix Kitten (APT34)
Region: Iran
Best known for: Australian parliament house attack, New York dam attack in 2013
Security experts believe the group operates primarily in the Middle East targeting chemical, energy, telecommunication, finance, and other industries as well as government institution in countries seen as competitors to Iran’s regional dominance such as Saudi Arabia and United Arab Emirates (UAE).
They believe Helix Kitten is not a group of freelancers from many countries in the world due to the use of communication infrastructure in Iran, as well as the Iranian regime’s goals.
Threats to a Local Business from state-sponsored cyber-attack
Since public decisions have such a direct impact on companies, it is in their best interests to remain updated about them and to continue to influence political decision-making and government policy. Businesses see and behave in their alliance with the government in a variety of ways.
Businesses have been a favorite target of state-sponsored attackers because they are the least well-defended entry point into a world, allowing for the extraction of money or intelligence as well as the injection of destruction. However, not every form of the company would be targeted.
Cyber-attacks that are successful can result in misplace sensitive data like credit card details, contact details, personal information. It helps the attackers to sell your client’s personal information on the dark web or annoy them.
Why companies should be wary of state-sponsored attacks?
Most companies aren’t vulnerable to state-sponsored cyber-attacks. These kinds of attacks become a potential threat only if you reach one or more of the following criteria:
1. If you work with the government or local council.
2. If you have a government contract that is still running.
3. If you achieve high profits.
4. If you have a service that, if it went down, would cause major disruption. (Medicine, gas, electricity, communication, transport, weapons, education)
5. If you run a business or have an office in a risky region. (Iran, Syria, Israel, Palestine)
6. If your company has access to highly confidential information.
How companies can survive from State-sponsored cyber-attacks
Basically, each company has to follow proper physical and logical security methods. Let’s see how it can be.
1. Having the fundamentals in place.
While the essentials will not protect you against state-sponsored attacks, they do give a minimum degree of protection that you should not be without.
2. Separate IT systems and data centers.
Isolating most valuable assets from the direct internet and you’re your general internal network increase the difficulty of stealing your intellectual property, bringing your IT system down, or interrupting your operations by a factor of ten.
However, because most organizations depend on fast access to the resources simply disconnecting all connections to your important IT assets is not an option. It is available through with some complex networking and tights management configurations and it greatly enhances your secure stability.
3. Secure your connection.
You must have at least one secure communication route. Like data, text, or voice, video. While the end to end encryption in applications like WhatsApp provides some protection.
4. Make security a part of your company’s culture.
While a checklist exercise like cyber essentials can get you started on the security you all need security embedded into your company’s culture to stand a fight against state-sponsored attackers. This can only be accomplished by implementing and following internationally recognized security standards like ISO27001.
Simulate attack and evaluate whether staff requires more training to address issues at the human level. Security must be held accountable to the board in order for priorities to be maintained.
5. Maintain the company’s technology supply chain.
If you’re employed on a state program or intend to bid on one, you’ve undoubtedly already taken efforts to limit your usage of potentially dangerous technology and software. However, if you haven’t yet mapped out what hardware or software you have in your infrastructure, you should conduct an audit.
Future developments in the area
State and state-sponsored hackers are increasingly targeting private sector firms in a variety of industries, including entertainment, health care, banking, telecommunication and education. Because of the widespread use of the internet for business along with insufficient cyber security procedures, state actors have been able to use cyber-attacks to achieve foreign policy goals some of which tactically include attacking private businesses.
Source: www.thomsonreuters.com
As a part of aa partnership with the World Economic Forum shared, a new extended research on configuring the future for our world, Thomson Reuters Labs have generated a visualization of this state-sponsored cyber-attacks dataset, illustrating the extent of the effect each attack depending on the number of targets affected. It has not represented the accused perpetrators of the attack, which are still being debated in certain situations. The frequency and range of these attacks are all growing, as seen in above graph.
I. United States — 65
II. United Kingdom — 34
III. Germany — 30
IV. India — 28
V. South Korea — 27
As this graph shows 22 nations including the US are accused of funding cyber attacking activities. State retaliation foe these attacks including those private organizations is increasing with state punishments and suspect charges.
Claiming cyber attacks to specific parties in complicated. Strategies for consistently and methodically doing so are developing. When private business is targeted by governmental actors this puts them in a tough position. They may be unable to predict when they will be targeted and to act appropriately when they are.
Finally, State-sponsored cyber attacks are an emerging and serious threat to private businesses. Posing and growing threat to industries that serve as ideal targets for resolving global disagreements.
Digital Silent Watchers
Behalf of a human, government in various states are getting benefits of these digital watchers. Why? They are invisible because of the digitality. No need ta pay salaries. It is just an executable file. They do phish digitally under some sort of commands which have written by state sponsored hackers. Once access has been secured, another common method is to remain silently installed on the network.
Some malware might alter its code after it has been installed to hide its content, making it more difficult for security solutions to track it down and remove it. It may then collect sensitive information invisibly, either extracting personal information on monitoring communications and giving it back to the hacker. This has the extra benefits of allowing the hacker to build a long term picture of the target peer including its regular connections, routings and ongoing issues among other things.
Aa a reason, security departments must be aware that the absence of immediate repercussions following a suspicious occurrence does not always indicate that the threat has passed. State- sponsored hacking is becoming a more widely recognized cyber risk, and businesses throughout the world must be prepared for a highly focused stealthy attack.
Many businesses are used to random cyber attacks, but many are unprepared to face a well-equipped and determined state-level adversary. Security operations directors must act now to solve this and guarantee that they have total insight into their security posture. With hacker’s techniques always developing, a throughout and agile threat response is essential. Neither governments nor businesses can afford to keep the back door open.
COVID-19 and State-Sponsored Attacks
Except for criminals, foreign government are taking advantage of the extraordinary circumstance by sending targeted phishing email to espionage targets in order to avoid regulations. Hackers are not afraid to say that they are up to.
Personalized emails with link to the epidemic are being used by a group suspected to be supported by China, North Korea and Russia to infect its target with malware or credentials. This COVID-19 outbreak proves once again that national security should not be limited to conventional military threats, but should also include the collecting of internet data by intelligence service, known as Signals Intelligence is moving its attention to new targets.
Political and military institutions are traditional targets because they can give information on a country’s political decision making processes or military capabilities. Cyber warfare is another key sector for intelligence services. At this moment, governments have to be interested in learning more about the virus’s spread. Various countries have approached for isolation and quarantine situations. And possible medicines as well as vaccinations.
As a result, intelligence services are increasingly targeting enterprises in the health care sector, biotechnology, pharmaceutical and transportation system. As a result, it’s hardly surprising that, in march 2020, WHO staff were targeted by spear-phishing email thought to have started in Iran. In May, the FBI and CISA issued a joint statement warning about cyber organizations linked to China.
Their mission is to gather digital intelligence on US institutes that do corona virus research. The goal is to find and get copyrighted material as well as public health data on immunizations, covid testing and treatments. They were allegedly partially successful in infiltrating the networks of these institutions. Two groups thought to be linked to China are accused of infecting individuals in Vietnam, Mongolia, and the Philippines with spyware by sending emails with attached papers containing authentic health information.
HACKTIVIST

"Hacktivist", a portmanteau of "hack" and "activism", was a term coined in 1996 by Omega, a member of the hacking coalition "Cult of the Dead Crow" (cDc). The term can be loosely defined as, "the ethically ambiguous use of computers and computer networks in order to affect the normal operation of other systems, motivated by a desire to protest or promote political ends."Oftentimes these events take the form of website defacements, denial-of-service attacks, information theft, website parodies, virtual sit-ins, typo squatting, and virtual sabotage.
The term has become popular among media outlets in recent years due to the rise of various politically motivated cyber attacks by groups such as Anonymous and LulzSec (now LulzSec Reborn) on governments and corporations across the world.
Cyber Terrorists

A cyber terrorist hacker is an individual or group that uses advanced computer skills to launch attacks on digital infrastructure, networks, or systems with the intention of causing fear, disruption, or harm for ideological, political, or religious motives.
Examples of cyber terrorist activities may include launching malware or ransomware attacks, disrupting critical infrastructure like power grids, conducting distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks, and infiltrating sensitive databases for unauthorized access or data manipulation. Notable incidents in the past have involved groups or individuals with political or ideological motivations, aiming to create chaos or promote their agenda through cyber means.
Sucide Hackers
A "suicide hacker" is a term often used to describe an individual who engages in cyber attacks with the knowledge that their actions may lead to severe legal consequences, including imprisonment. The term is metaphorical, drawing parallels with the concept of a suicide bomber. Essentially, a suicide hacker may prioritize their cause or ideology over personal safety and freedom.
An example could be an individual or group carrying out a high-profile and destructive cyber attack, fully aware of the likelihood of facing legal repercussions, but driven by strong ideological or political motivations. The term underscores the extreme commitment some hackers may have to their causes, even at the expense of personal consequences.
Spy Hacker
A "spy hacker" refers to an individual or group of hackers who engage in activities aimed at unauthorized acquisition of sensitive information, typically for espionage or intelligence purposes. These individuals may infiltrate computer systems, networks, or databases to gather confidential data, such as government secrets, corporate information, or personal details.
Spy hackers often operate covertly and may be affiliated with state-sponsored cyber espionage programs, intelligence agencies, or criminal organizations. Their primary goal is to collect valuable information while remaining undetected, and their activities can have significant implications for national security, businesses, and individuals.
Spy hackers engage in various activities to achieve their goals, including:
Infiltration: Gaining unauthorized access to computer systems, networks, or databases by exploiting vulnerabilities or using sophisticated techniques like phishing or malware attacks.
Surveillance: Monitoring and collecting data from target systems to gather valuable information, such as classified documents, proprietary business data, or sensitive personal details.
Eavesdropping: Intercepting and monitoring communication channels, whether it be email, messaging platforms, or other forms of electronic communication, to gather intelligence.
Covert Operations: Conducting operations with a high degree of stealth and discretion to avoid detection while extracting information over an extended period.
Manipulation: Altering or influencing data within a system to mislead or gain a strategic advantage, whether it's spreading disinformation or manipulating financial or political information.
Persistence: Maintaining long-term access to compromised systems to continue extracting valuable information over an extended period.
Spy hackers can be motivated by political, economic, or military objectives, and their activities can have far-reaching consequences, impacting national security, economic stability, and individual privacy.
One notable example of state-sponsored cyber espionage involves the Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) group known as APT29 or Cozy Bear. This group is believed to be associated with Russian intelligence agencies.
In 2015, APT29 gained widespread attention for infiltrating the Democratic National Committee's (DNC) computer network. The hackers were accused of conducting a sophisticated cyber espionage campaign, during which they exfiltrated sensitive political information, emails, and documents. The stolen data was later leaked, influencing the 2016 U.S. presidential election.
This incident highlighted the capabilities of spy hackers in carrying out targeted and politically motivated cyber attacks, aiming to influence or gain insights into sensitive political processes.


Comments
Post a Comment